ZR36050 Просмотр технического описания (PDF) - Unspecified
Номер в каталоге
Компоненты Описание
Список матч
ZR36050 Datasheet PDF : 52 Pages
| |||
ADVANCE INFORMATION
ZR36050
FUNCTIONAL OVERVIEW
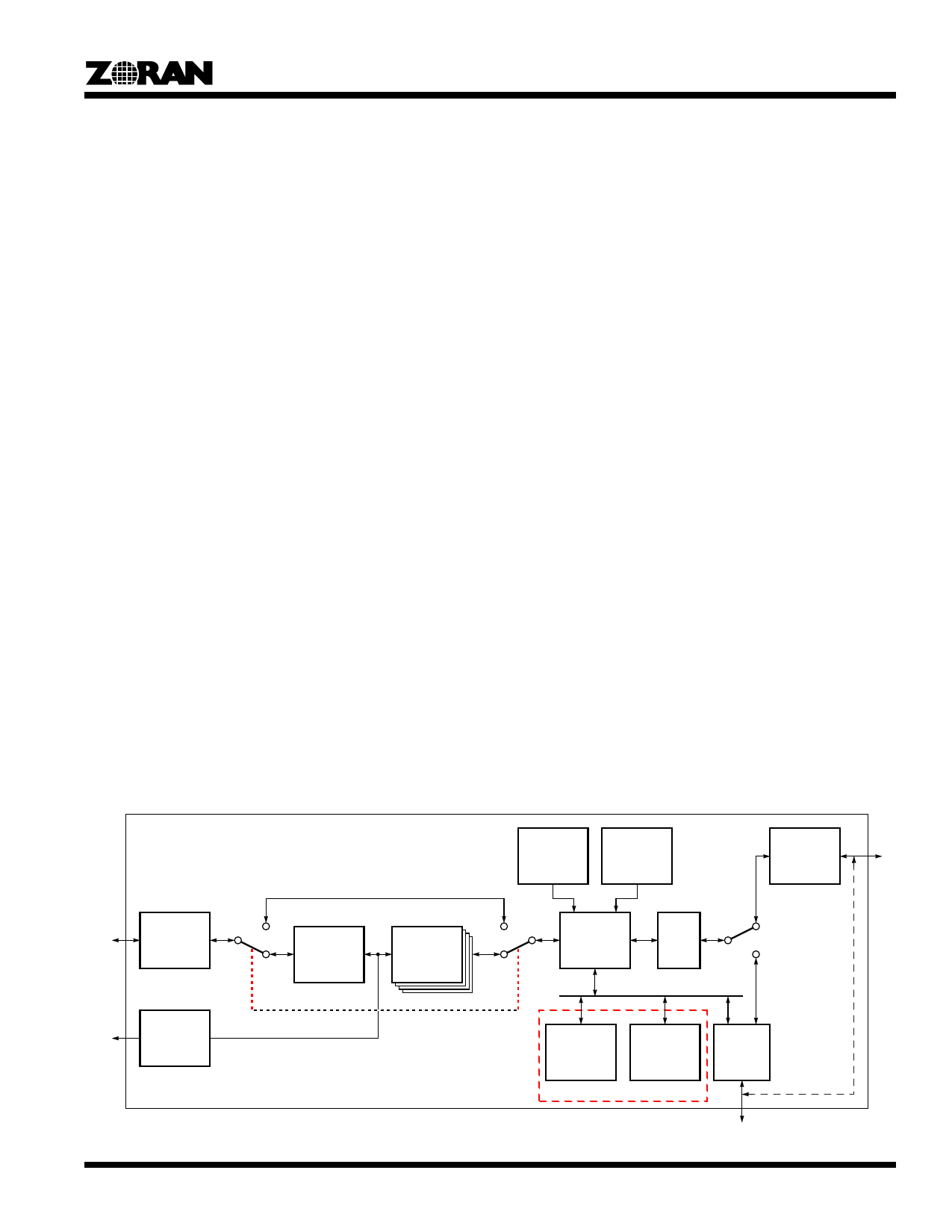
Figure 2 is a functional block diagram of the ZR36050 JPEG
Image Compression Processor. The ZR36050 consists of two
major processing units, the DCT Unit and the Encoding/Decod-
ing Unit, with their associated buffers, an Internal Memory for
data exchange with the host processor, special internal storage
for tables, and three bus interfaces.
During a compression operation, image data flows in through the
Pixel Interface and compressed data flows out through either the
Compressed Data Interface or the Host Interface. The direction
of data flow is reversed during an expansion operation.
Pixel Interface
In compression of an image, the source of the image data
samples is typically a strip, field, or frame buffer (see Figure 3,
for example). The external image buffer control logic writes the
image samples into the ZR36050 via the Pixel Interface, which
operates synchronously, transferring each sample in on the
rising edge of the clock. A synchronizing signal, driven by the
buffer control logic, indicates to the Pixel Interface when valid
samples are being presented to it.
In JPEG Baseline compression, each color component of the
image must be partitioned into blocks of 8 x 8 samples. The
image data enters the Pixel Interface one component block at a
time, each block starting with the top left sample, scanned by
rows, and ending with the bottom right sample. As required by
the JPEG Baseline standard, the blocks are grouped into a
repeating pattern of Minimum Coded Units, or MCU’s. For
example, in an interleaved scan of Y, U, and V components, with
4:2:2 subsampling, the MCU consists of two blocks of Y, one
block of U, one block of V, and image blocks enter the device in
the following order:
Y0 Y1 U0 V0 Y2 Y3 U1 V1 Y4 Y5 U2 V2 ....
where each component designator (Y, U or V) represents a block
of 64 samples, and the subscript indicates the block index.
On the other hand, in JPEG Lossless compression, the image
components enter the Pixel Interface in a normal raster. In the
above example, the MCU then consists of two Y samples, one U
sample and one V sample.
When outputting expanded image data, the Pixel Interface
drives the synchronizing signal and the pixel data bus.
DCT Unit and Coefficient Buffers
In JPEG Baseline compression, the DCT Unit transforms each
component block into 64 DCT coefficients, and writes the coeffi-
cients into the next available DCT Coefficient Block Buffer. At the
same time, it outputs the DCT coefficients on the Coefficient
Bus. In expansion, it performs the inverse DCT, whenever a
complete block of DCT coefficients is available in the buffer.
Because JPEG Lossless compression uses a spatial domain
algorithm, when the ZR36050 operates in Lossless mode, the
DCT Unit and Coefficient Block Buffers are bypassed. There is
also a Fast Preview mode (described later) for expansion of
JPEG Baseline compressed data, in which the Inverse DCT Unit
and Coefficient Buffers are also bypassed.
Encoding/Decoding Unit, Code Buffer
The Encoding/Decoding Unit performs the remainder of the
JPEG compression and also formats the compressed data —
including the insertion of JPEG bit and byte stuffing, JPEG
markers, marker segments and their associated parameters.
The compressed data conforms completely to the JPEG format
and no reformatting or additional parameter insertion is needed.
Pixel
Interface
Coefficient
Bus
Lossless and Fast
Preview Modes
Baseline
Modes
Forward and
Inverse DCT
Unit
DCT
Coefficient
Block Buffers
Quantization
Tables Store
Huffman
Tables Store
Encoding
and
Decoding
Unit
Code
Buffer
Compressed
Data
Interface
Master
Mode
16-Bit
Mode
Slave and
DMA Modes
Control
Registers
Section
JPEG Marker
Segments
Section
Internal Memory
Host
Interface
Figure 2. ZR36050 Functional Block Diagram
7