ZR36050 Просмотр технического описания (PDF) - Unspecified
Номер в каталоге
Компоненты Описание
Список матч
ZR36050 Datasheet PDF : 52 Pages
| |||
ADVANCE INFORMATION
ZR36050
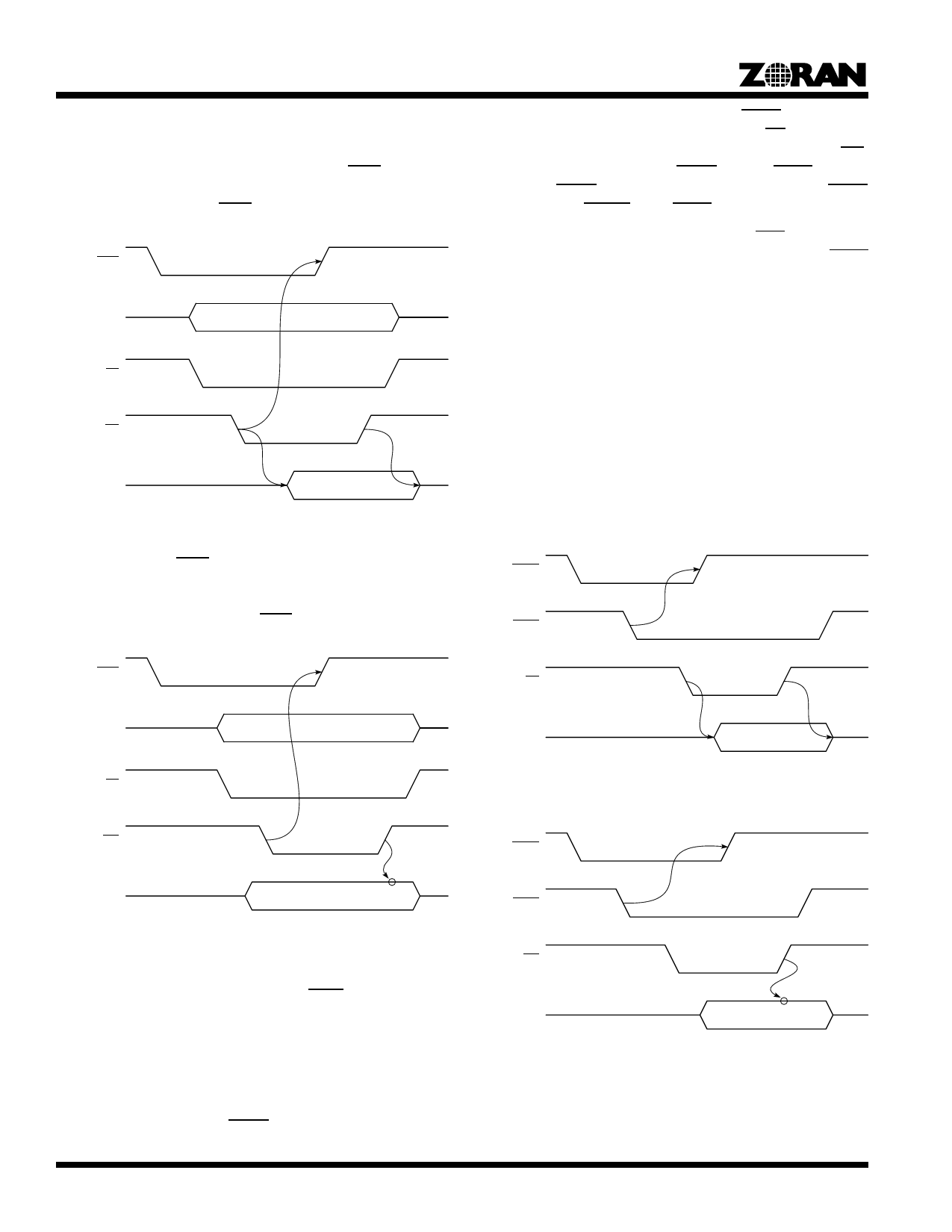
In encoding, the ZR36050 indicates that 8 or 16 bits of com-
pressed data are ready to be read out, by setting the DATRDY
bit in the STATUS_1 register. If the corresponding bit in
INT_REQ_1 is set, the Host Interface activates DINT. When the
host reads the Compressed Data register, the ZR36050 clears
DATRDY and deactivates DINT, as shown in Figure 11.
DINT
ADDR
30 (hex)
CS
RD
DATA
(or DATA/CODE)
Figure 11. Slave Read of Compressed Data in Encoding
In decoding, active DINT indicates that the ZR36050 is ready to
receive the next 8 or 16 bits of compressed data. When the host
writes the data in the Compressed Data register, the ZR36050
clears DATRDY and deactivates DINT, as shown in Figure 12.
controller acknowledges the transfer with DACK. In encoding,
the DMA controller reads the data by activating RD. In decoding,
the Host Interface latches the data on the trailing edge of WR.
The ZR36050 does not output a DREQ until the DACK signal to
the previous DREQ has been deactivated. In both cases DREQ
is deactivated by RESET, or by DACK.
In the encoding modes, the ZR36050 outputs END only after the
EOI marker (FFD9) has been read and its corresponding DACK
signal has been deactivated.
The transfers can be 8 or 16 bits wide, as specified by the BSWD
bit in the HARDWARE register. In 16 bit transfers, the CODE bus
acts as an extension of the DATA bus. The lower numbered byte
(the byte that would have been transferred earlier in 8 bit trans-
fers) is read or written on either the CODE or DATA bus,
depending on the BELE bit in the HARDWARE register. In 16-bit
transfers, if the last transfer of compressed data requires only
one byte, the ZR36050 appends a FF byte to complete the 16
bits in encoding, and in decoding, the host can append an arbi-
trary byte.
Figure 13 and Figure 14, respectively, show DMA Compressed
Data Transfer cycles in encoding and decoding.
DREQ
DACK
DINT
RD
ADDR
CS
30 (hex)
DATA
(or DATA/CODE)
Figure 13. DMA Read of Compressed Data in Encoding
WR
DREQ
DATA
(or DATA/CODE)
DACK
Figure 12. Slave Write of Compressed Data in Decoding
Note that if the DATRDY bit in the INT_REQ_1 register is not set,
the Host Interface does not activate DINT. The host can,
however, still determine whether new compressed data is ready
or needed, by polling the STATUS_1 register to determine the
state of DATRDY.
DMA Compressed Data Transfer
In DMA mode, the Host Interface requests a DMA Compressed
Data Transfer by activating DREQ, and the host system’s DMA
WR
DATA
(or DATA/CODE)
Figure 14. DMA Write of Compressed Data in Decoding
20