AD537 Просмотр технического описания (PDF) - Analog Devices
Номер в каталоге
Компоненты Описание
Список матч
AD537 Datasheet PDF : 8 Pages
| |||
AD537
SYNCHRONOUS OPERATION
The SYNC terminal at pin 2 of the DIP package can be used to
synchronize a free running AD537 to a master oscillator, either
at a multiple or a sub-multiple of the primary frequency. The
preferred connection is shown in Figure 10. The diodes are used
to produce the proper drive magnitude from high level signals.
The SYNC terminal can also be used to shut off the oscillator.
Shorting the terminal to +VS will stop the oscillator, and the
output will go high (output NPN off).
VSYNC
CS
1000pF
VIN
NOTE: IF VSYNC >2V p-p
USE THIS LIMITER
CS
VSYNC
2
10k
1N4148
AD537
1
14
fOUT
R
2
DRIVER 13
+VS
3
12
4
BUF
CURR-
TO-FREQ
11
CT
CONV
5
10
6
VT PRECISION
9
VOLTAGE
7
VR REFERENCE
8
Figure 10. Connection for Synchronous Operation
Figure 11 shows the maximum pull-in range available at a given
signal level; the optimum signal is a 0.8 to 1.0 volt square wave;
signals below 0.1 volt will have no effect; signals above 2 volts
p-p will disable the oscillator. The AD537 can normally be syn-
chronized to a signal which forces it to a higher frequency up to
30% above the nominal free-running frequency, it can only be
brought down about 1–2%.
FREQ
CONTROL
INPUT
0 TO –10V
LOGIC
GND
1
DEC/
SYN
2
3
10k
4
5
VTEMP 6
VREF 7
AD537
OUTPUT
14
DRIVER 13 +VS 3.9V
CURR
BUF
-TO-
FREQ
CONV
VT
PRECISION
VOLTAGE
REFERENCE
VR
12
CAP
11
0.01µF
10
SIGNAL
VOS INPUT
9
±12V PK
8 –VS
RECOVERED
FREQUENCY
SIGNAL
+15V
1 14 12
2
11
6
10
78
COM-
POSITE
ERROR
SIGNAL
±1V PK
–15V
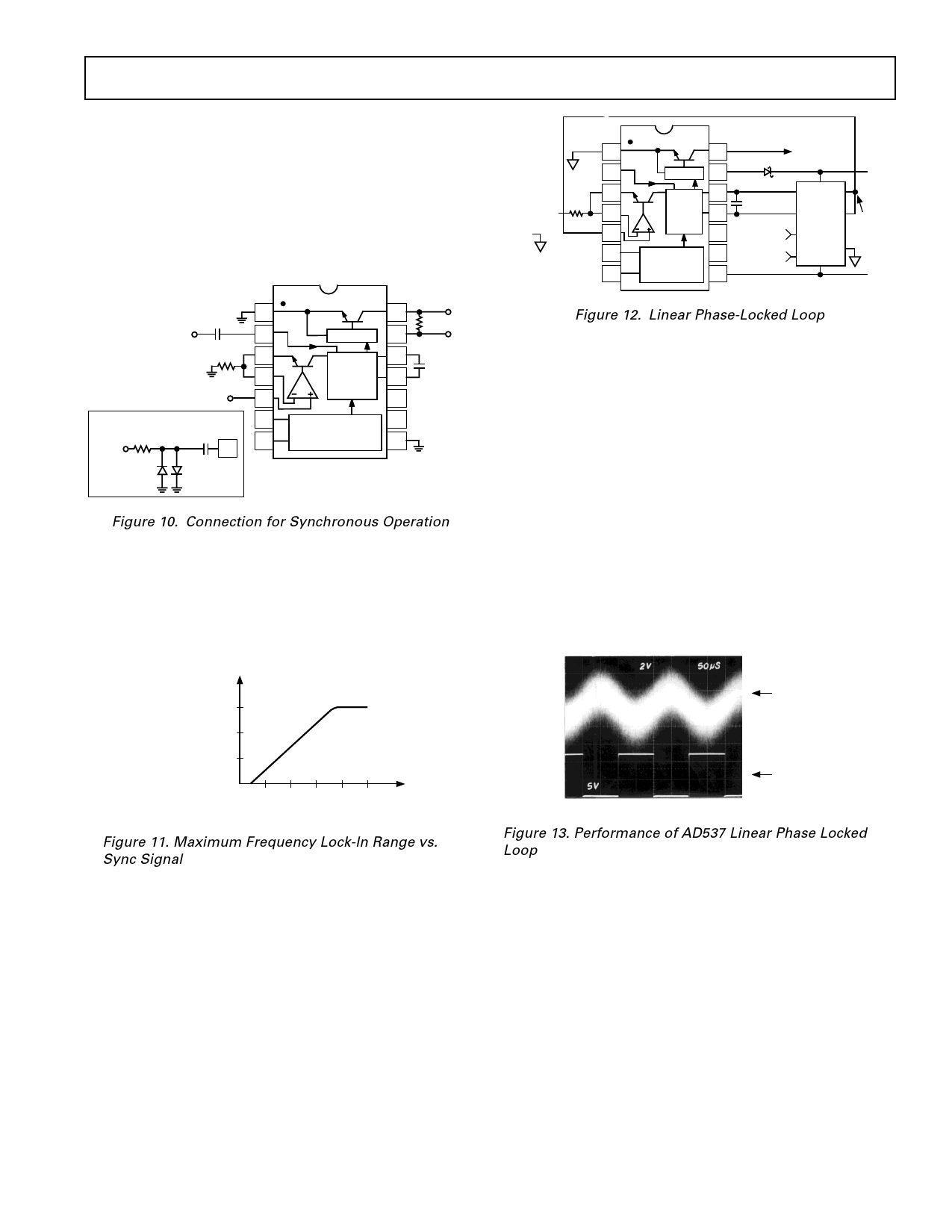
Figure 12. Linear Phase-Locked Loop
Noise on the input signal affects the loop operation only slightly;
it appears as noise in the timing current, but this is averaged out
by the timing capacitor. On the other hand, if the input fre-
quency changes there is a net error voltage at Pin 5 which acts
to bring the oscillator back into quadrature. Thus, the output at
Pin 14 is a noise-free square-wave having exactly the same fre-
quency as the input signal. The effectiveness of this circuit can
be judged from Figure 13 which shows the response to an input
of 1 V rms 1 kHz sinusoid plus 1 V rms Gaussian noise. The
positive supply to the AD537 is reduced by about 4 V in order
to keep the voltages at Pins 11 and 12 within the common-mode
range of the AD534.
Since this is also a first-order loop the circuit possesses a very
wide capture range. However, even better noise-integrating
properties can be achieved by adding a filter between the multi-
plier output and the VCO input. Details of suitable filter charac-
teristics can be found in the standard texts on the subject.
30%
FREQUENCY
LOCK-IN 20%
RANGE
10%
0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0
VSYNC SQUARE-WAVE INPUT VOLTS p-p
Figure 11. Maximum Frequency Lock-ln Range vs.
Sync Signal
LINEAR PHASE LOCKED LOOP
The phase-locked-loop F/V circuit described earlier operates
from an essentially noise-free binary input. PLL’s are also used
to extract frequency information from a noisy analog signal. To
do this, the digital phase-comparator must be replaced by a lin-
ear multiplier. In the implementation shown in Figure 12, the
triangular waveform appearing across the timing capacitor is
used as one of the multiplier inputs; the signal provides the
other input. It can be shown that the mean value of the multi-
plier output is zero when the two signals are in quadrature. In
this condition, the ripple in the error signal is also quite small.
Thus, the voltage at Pin 5 is essentially zero, and the frequency
is determined primarily by the current in the timing resistor,
controlled either manually or by a control voltage.
1V RMS SIGNAL
+1V RMS NOISE
OUTPUT
Figure 13. Performance of AD537 Linear Phase Locked
Loop
By connecting the multiplier output to the lower end of the tim-
ing resistor and moving the control input to Pin 5, a high resis-
tance frequency-control input is made available. However, due
to the reduced supply voltage, this input cannot exceed +6 V.
TRANSDUCER INTERFACE
The AD537 was specifically designed to accept a broad range of
input signals, particularly small voltage signals, which may be
converted directly (unlike many V-F converters which require
signal preconditioning). The 1.00 V stable reference output is
also useful in interfacing situations, and the high input resis-
tance allows nonloading interfacing from a source of varying
resistance, such as the slider of a potentiometer.
REV. C
–7–