HIP6019B Просмотр технического описания (PDF) - Intersil
Номер в каталоге
Компоненты Описание
Список матч
HIP6019B Datasheet PDF : 15 Pages
| |||
HIP6019B
indicates when CSS is fully charged (UP signal), such that an
under-voltage event on either linear output (FB3 or FB4) is
ignored until after the soft-start interval (approximately T3 in
Figure 6). At start-up, this allows VOUT3 and VOUT4 to slew
up over increased time intervals, without generating a fault.
Cycling the bias input voltage (+12VIN on the VCC pin) off
then on resets the counter and the fault latch.
LUV
OC1
OC2
0.15V +
-
SS
+
4V -
OV
OVER
CURRENT
LATCH
SQ
R
UP
INHIBIT
S
COUNTER
R
FAULT VCC
LATCH
SQ
POR
R
FAULT
FIGURE 7. FAULT LOGIC - SIMPLIFIED SCHEMATIC
Over-Voltage Protection
During operation, a short on the upper MOSFET (Q1)
causes VOUT1 to increase. When the output exceeds the
over-voltage threshold of 115% of DACOUT, the over-
voltage comparator trips to set the fault latch and turns Q2
on as required in order to regulate VOUT1 to 1.15 x
DACOUT. This blows the input fuse and reduces VOUT1.
The fault latch raises the FAULT/RT pin close to VCC
potential.
A separate over-voltage circuit provides protection during
the initial application of power. For voltages on the VCC pin
below the power-on reset (and above ~4V), VOUT1 is
monitored for voltages exceeding 1.26V. Should VSEN1
exceed this level, the lower MOSFET (Q2) is driven on, as
needed to regulate VOUT1 to 1.26V.
Over-Current Protection
All outputs are protected against excessive over-currents.
Both PWM controllers use the upper MOSFET’s
on-resistance, rDS(ON) to monitor the current for protection
against shorted outputs. The linear regulator monitors the
current of the integrated power device and signals an over-
current condition for currents in excess of 230mA.
Additionally, both the linear regulator and the linear
controller monitor FB3 and FB4 for under-voltage to protect
against excessive currents.
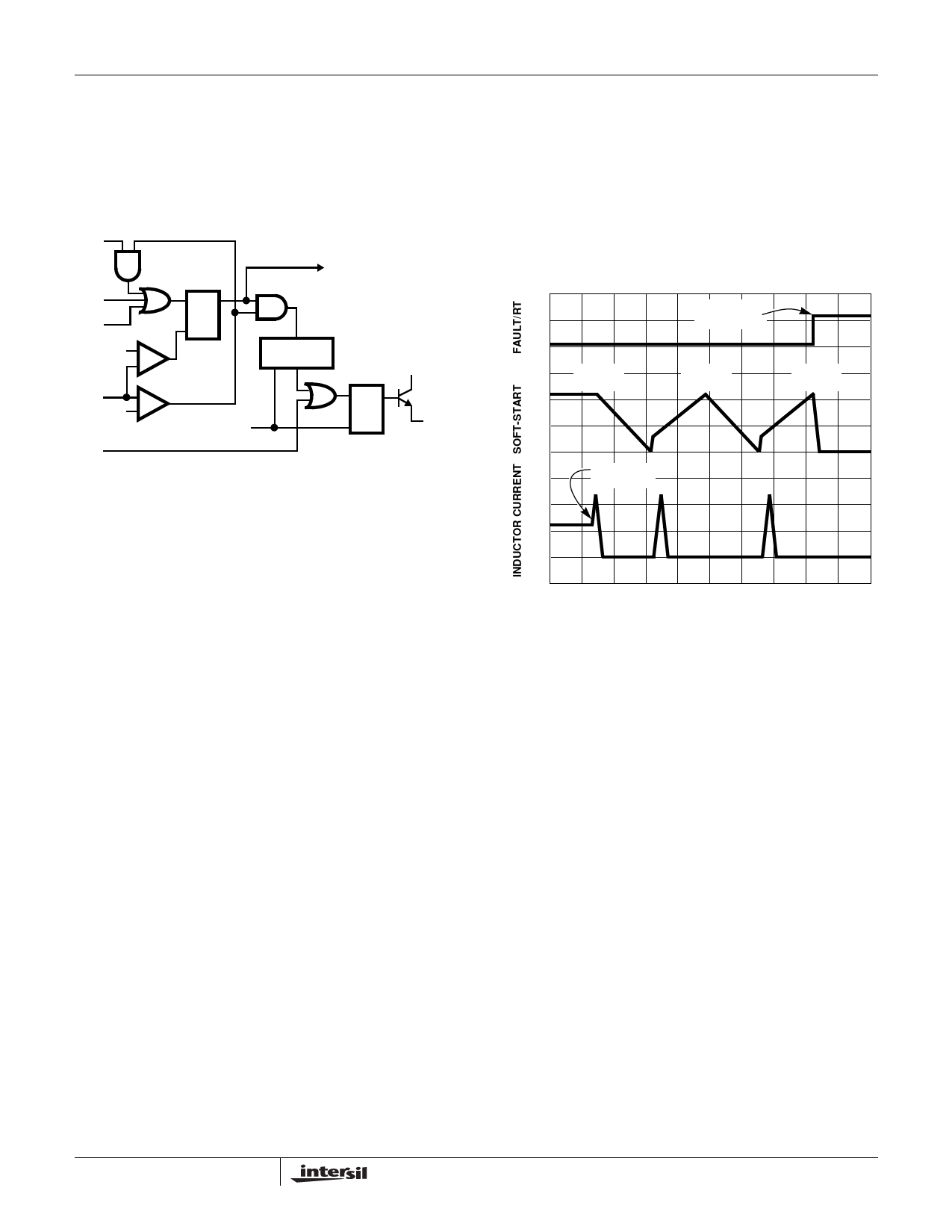
Figures 8 and 9 illustrate the over-current protection with an
overload on OUT2. The overload is applied at T0 and the
current increases through the output inductor (LOUT2). At time
T1, the OVER-CURRENT2 comparator trips when the voltage
across Q3 (ID • rDS(ON)) exceeds the level programmed by
ROCSET. This inhibits all outputs, discharges the soft-start
capacitor (CSS) with a 11µA current sink, and increments the
8
counter. CSS recharges at T2 and initiates a soft-start cycle
with the error amplifiers clamped by soft-start. With OUT2 still
overloaded, the inductor current increases to trip the over-
current comparator. Again, this inhibits all outputs, but the
soft-start voltage continues increasing to 4V before
discharging. The counter increments to 2. The soft-start cycle
repeats at T3 and trips the over-current comparator. The SS
pin voltage increases to 4V at T4 and the counter increments to
3. This sets the fault latch to disable the converter. The fault is
reported on the FAULT/RT pin.
FAULT
10V
REPORTED
0V
COUNT
=1
4V
COUNT
=2
COUNT
=3
2V
0V
OVERLOAD
APPLIED
0A
T0 T1
T2
T3
T4
TIME
FIGURE 8. OVER-CURRENT OPERATION
The PWM1 controller and the linear regulator operate in the
same way as PWM2 to over-current faults. Additionally, the
linear regulator and linear controller monitor the feedback
pins for an under-voltage. Should excessive currents cause
FB3 or FB4 to fall below the linear under-voltage threshold,
the LUV signal sets the over-current latch if CSS is fully
charged. Blanking the LUV signal during the CSS charge
interval allows the linear outputs to build above the under-
voltage threshold during normal start-up. Cycling the bias
input power off then on resets the counter and the fault latch.
FN4587.1
April 13, 2005