RT9181CB Просмотр технического описания (PDF) - Richtek Technology
Номер в каталоге
Компоненты Описание
Список матч
RT9181CB Datasheet PDF : 10 Pages
| |||
RT9181
Preliminary
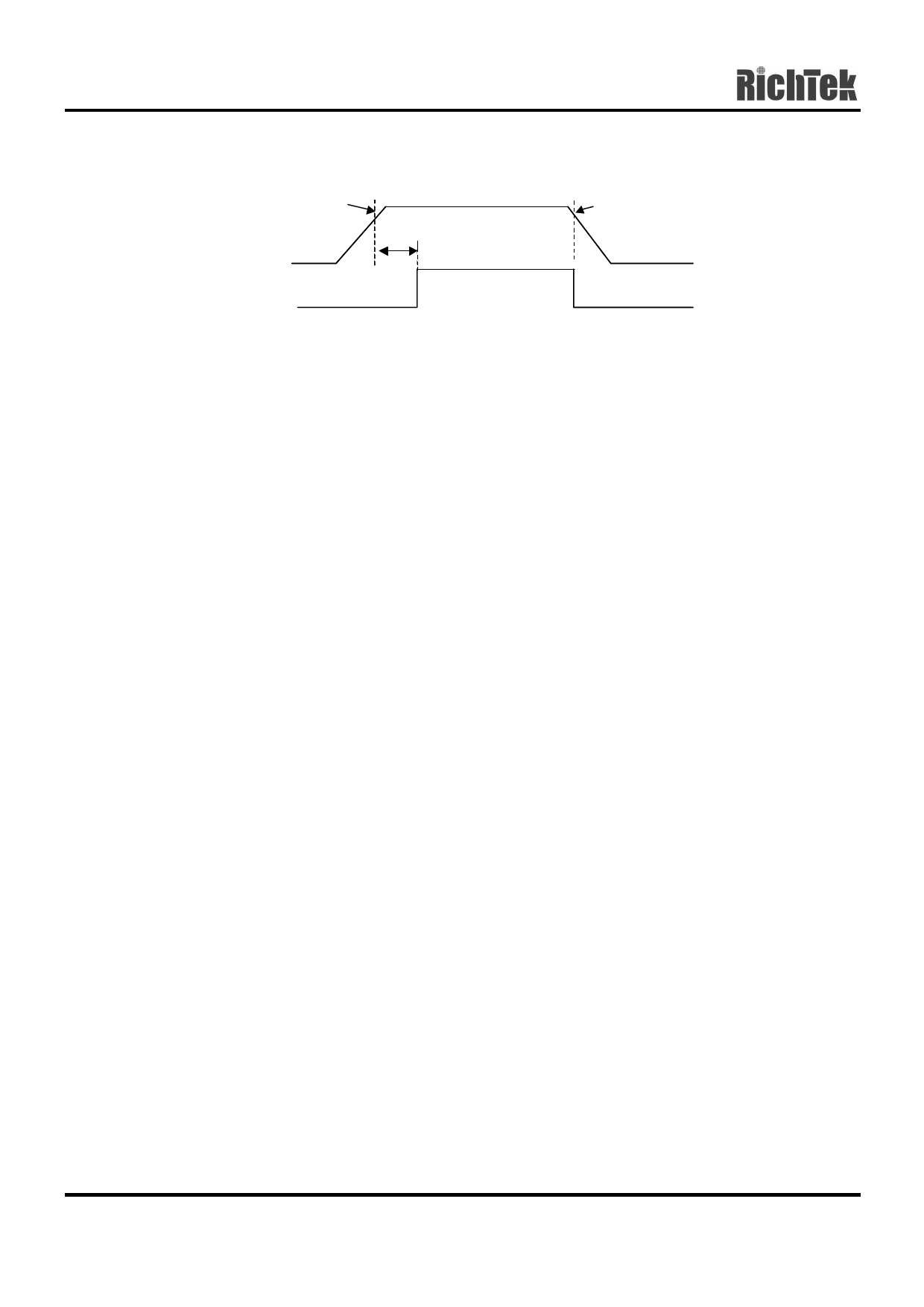
Timing Diagram
90% max of VOUT (normal)
VPOGH
td(POG) 2.0ms typ.
VOUT
POG
VPOGL
85% min
Application Guides
CE/Shutdown
The RT9181 is enabled by driving the CE input high,
and shutdown by pulling the input low. If this feature
is not to be used, the CE input should be tied to VIN
to keep the regulator enabled at all times (the CE
input must not be left floating).
Internal P-Channel Pass Transistor
The RT9181 features a P-channel MOSFET pass
transistors. It provides several advantages over
similar designs using PNP pass transistors, including
longer battery life. The P-channel MOSFET requires
no base drive, which reduces quiescent current
considerably. PNP-based regulators waste
considerable current in dropout when the pass
transistor saturates, They also use high base-drive
currents under large loads. The RT9181 does not
suffer from these problems and consume only 160µA
of quiescent current whether in dropout, light-load, or
heavy-load applications.
Power Good
The power good output is an open-drain output. It is
designed essentially to work as a power-on reset
generator once the regulated voltage was up or a
fault condition. The output of the power good drives
low when a fault condition occurs. The power good
output come back up once the output has reached
90% of its nominal value and a 2.0ms (typ.) delay
has passed. See Timing Diagram. The output voltage
level will be drooped at the fault conditions including
current limit, thermal shutdown, or shutdown and
triggers the POG detector to alarm a fault condition.
This output is fed into an on-board delay circuitry that
www.richtek-ic.com.tw
6
drives the open drain transistor to indicate a fault.
Because at shutdown mode, a fault condition occurs
by pulling the POG output low, it will sink a current
from the open drain and the external power.
Selecting a suitable pulling resistance will be well to
control this dissipated power.
Current Limit and Thermal Protection
The RT9181 includes a current limit structure which
monitor and control the pass transistor’s gate voltage
limiting the guaranteed maximum output current to
150mA minimum.
Thermal-overload protection limits total power
dissipation in the RT9181. When the junction
temperature exceeds TJ = +150°C, the thermal
sensor signals the shutdown logic turning off the
pass transistor and allowing the IC to cool. The
thermal sensor will turn the pass transistor on again
after the IC’s junction temperature cools by 20°C,
resulting in a pulsed output during continuous
thermal-overload conditions. Thermal-overloaded
protection is designed to protect the RT9181 in the
event of fault conditions. Do not exceed the absolute
maximum junction-temperature rating of TJ = +125°C
for continuous operation. The output can be shorted
to ground for and indefinite amount of time without
damaging the part by cooperation of current limit and
thermal protection.
Operating Region and Power Dissipation
The maximum power dissipation of RT9181 depends
on the thermal resistance of the case and circuit
board, the temperature difference between the die
junction and ambient air, and the rate of air flow. The
DS9181-00 February 2002